
Eligibility for Coverdell Education Savings AccountsĮarnings within a Coverdell education savings account and distributions to pay for qualified education expenses are tax-free. Married taxpayers who file as married filing separately are ineligible. To qualify for interest-free treatment, the bond holder must have income under income phaseouts of $91,850 to $106,850 for single filers and $137,800 to $167,800 for married filing jointly in the year during which you cash in the bonds or roll them over into a 529 plan.

The savings bonds must have been issued in the taxpayer’s name, who must have been at least 24 years old before the bond issue date.
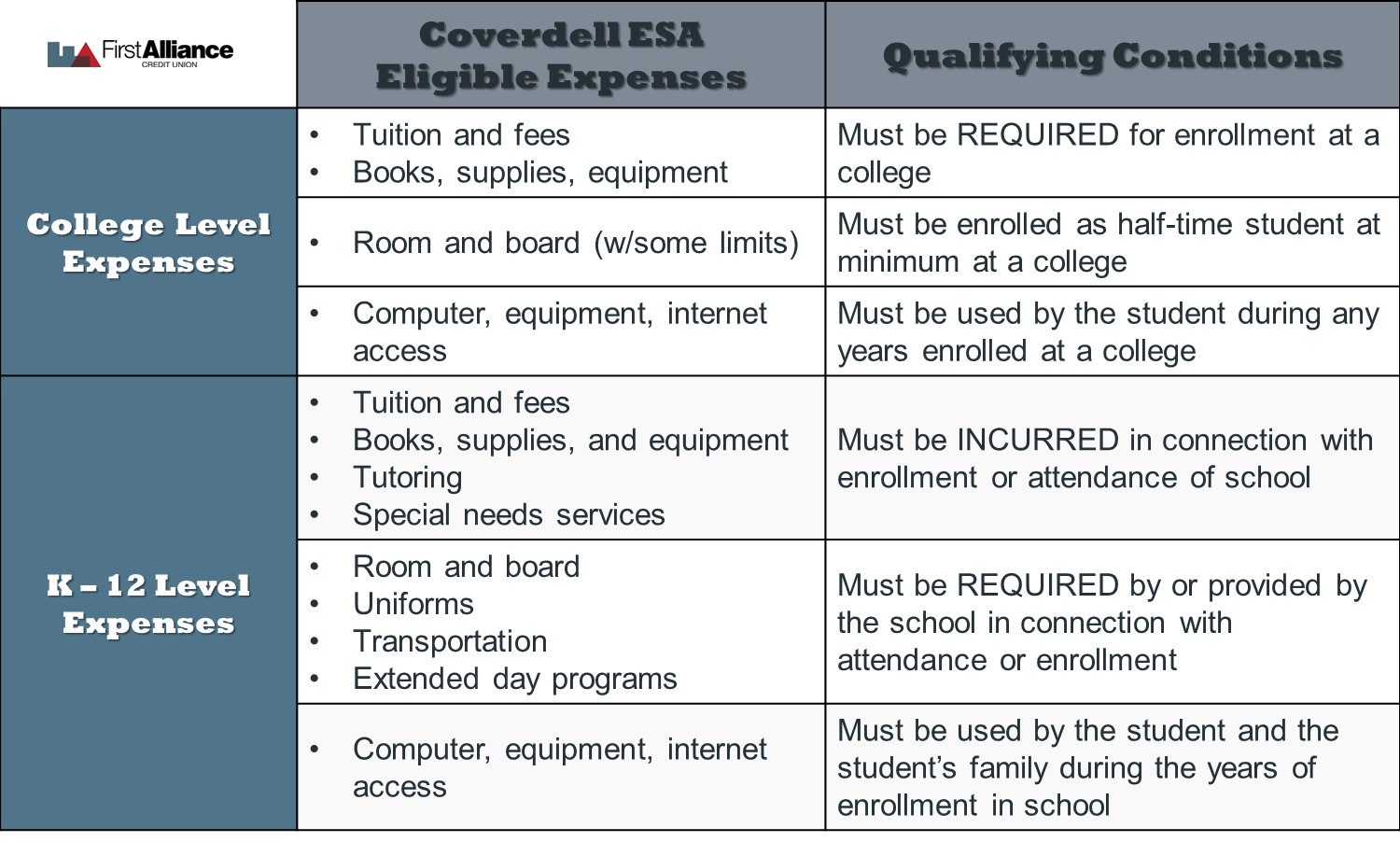
Qualified education expenses computer series#
Savings Bonds issued in 1990 or a later year and Series I U.S. Qualified education savings bonds include Series EE U.S. The qualified expenses are reduced by the amount of tax-free education benefits, the AOTC or LLTC, uses for the same expenses. The beneficiary of the 529 plan, prepaid tuition plan or Coverdell must be the taxpayer, the taxpayer’s spouse or the taxpayer’s dependent.

The qualified education expenses must have been paid for the education of the taxpayer, the taxpayer’s spouse or the taxpayer’s dependent. Qualified education expenses include tuition and required fees. Interest on qualified education savings bonds is tax-free when redeemed to pay for qualified education expenses or rolled over into a 529 college savings plan, prepaid tuition plan or Coverdell education savings account. Eligibility for the Education Savings Bond Program The student loan interest deduction has income phaseouts of $75,000 to $90,000 for single filers and $155,000 to $185,000 for married filing jointly. Interest paid by others is counted as though it were paid by the borrower. The taxpayer must have been legally obligated to pay the interest on the student loan. The borrower must not be claimed on someone else’s federal income tax return. The income phaseouts for the American Opportunity Tax Credit and Lifetime Learning Tax Credit are not adjusted for inflation. The student does not need to be enrolled on at least a half-time basis.Ĭoordination restrictions prevent claiming both the AOTC and LLTC for the same student in the same year.īoth tax credits have income phaseouts of $80,000 to $90,000 for single filers and $160,000 to $180,000 for married filing jointly. The LLTC is available for an unlimited number of years, and is often used for graduate students and continuing education.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
